Semantic SEO is the modern approach to search engine optimization that goes beyond traditional keyword matching to understand user intent, context, and meaning behind search queries. With search engines becoming smarter, it’s no longer enough to focus only on specific keywords. Instead, the future of SEO is about making content more meaningful and relevant to both users and search engines.
By using techniques like latent semantic indexing SEO and semantic markup SEO, you can improve your rankings and boost visibility. Google’s understanding of Google search semantics SEO has evolved significantly, allowing the search engine to evaluate content based on the overall context rather than isolated keywords.
In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of semantic SEO, why it’s important, and how you can implement it on your website to stay ahead in the digital space.
What Is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO refers to optimizing your content for search engines by understanding the meaning behind the words users type in the search bar. Instead of focusing solely on exact match keywords, semantic SEO emphasizes context and user intent. Google, for instance, doesn’t just look at keywords but analyzes how they relate to the user’s search intent, making your content more relevant to a wider audience.
What is Semantic SEO in Practice?
When you optimize for semantic SEO, you make sure your content answers not only the search query but the underlying question or need behind it. For example, if someone types in “how to improve SEO,” semantic SEO would suggest targeting related topics such as link-building, content marketing, and keyword strategy, not just the phrase “improve SEO.”
Benefits of Semantic SEO:
- Enhanced Search Visibility: Aligning with user intent means your content ranks better for relevant queries.
- Improved User Experience: Content that answers questions in-depth leads to higher user satisfaction.
- Better Rankings: By understanding relationships between words, you improve rankings not just for primary keywords, but related terms as well.
Key Concept:
Google uses advanced techniques like latent semantic indexing SEO and semantic markup SEO to interpret and rank content based on meaning rather than just keywords. This allows your content to be ranked for a broader range of related terms, improving its discoverability.
Why Is Semantic SEO Important?
The search engine landscape has evolved significantly in the last decade. Google’s algorithms now understand the context of a query, not just the words in it. With updates like Hummingbird, RankBrain, and BERT, Google’s algorithms are focused on Google search semantics SEO to better comprehend how words work together and their relevance to a searcher’s intent.
Evolving Search Engines:
- Google Search Semantics SEO: With semantic search, Google can now interpret complex queries by understanding the meaning of the words in relation to one another. This means that ranking is no longer about matching exact keywords but about presenting content that best answers a user’s underlying question.
- Hummingbird: This algorithm update allowed Google to shift from focusing purely on keywords to understanding the meaning behind the query.
- RankBrain: This machine learning system processes queries to deliver results based on contextual understanding, further enhancing the semantic SEO process.
- BERT: This update helps Google understand the nuances and context of words in search queries, improving the search engine’s interpretation of user intent.
Competitive Edge:
Focusing on semantic SEO gives you a competitive edge because it ensures your content is designed to match the true intent behind users’ searches. By doing so, you improve your chances of ranking not just for one keyword, but a whole set of related queries.
Core Principles of Semantic SEO
Mastering semantic SEO involves understanding several core principles that ensure your content aligns with both user intent and search engine algorithms.
1. Understanding Search Intent
Understanding search intent is crucial for any semantic SEO strategy. There are four primary types of search intent:
- Informational Intent: The user seeks information, such as “what is semantic SEO?”
- Navigational Intent: The user wants to go to a specific website or page, like “Facebook login.”
- Transactional Intent: The user is ready to buy, such as “buy SEO tools.”
- Commercial Investigation: The user is in the research phase, exploring options, such as “best SEO services.”
By understanding these intents, you can create content that directly answers what users are looking for.
2. Using Semantic Markup
Semantic markup SEO involves using structured data to help search engines understand your content better. Tools like schema markup allow you to tag your content so Google can interpret its meaning more accurately, which helps improve its ranking potential.
Benefits of Semantic Markup SEO:
- Helps search engines understand content’s structure and meaning.
- Improves visibility with rich snippets (e.g., reviews, prices).
- Enhances search rankings by providing more detailed information about your content.
3. Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI)
Latent Semantic Indexing SEO (LSI) is an essential component of semantic SEO. LSI helps search engines discover related words and concepts, ensuring content is understood in a broader context. For example, if your content is about “SEO,” related terms like “backlinks,” “content marketing,” and “keyword strategy” would help search engines understand the full scope of your content.
Using LSI helps improve rankings because search engines can connect your content with a wider set of related search terms.
How to Implement Semantic SEO on Your Website
Now that you understand the importance of semantic SEO, here’s how to apply it effectively:
Step 1: Conducting Topic Research
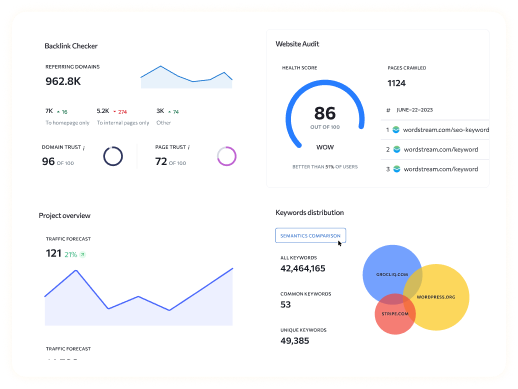
Begin by researching related keywords and topics. Tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Google Trends will help you identify topics that are relevant to your primary keywords. You can also use Grocliq to find latent semantic indexing SEO keywords that will help improve the overall semantic value of your content.
Step 2: Writing Comprehensive Content
Your content should cover a wide array of related topics, ensuring that it answers a user’s question from all angles. Don’t just use the primary keyword; integrate LSI keywords to help Google understand the full context.
Step 3: Using Structured Data
Implement semantic markup SEO using structured data. This makes it easier for search engines to categorize and display your content in search results, increasing your chances of being featured in rich snippets.
Step 4: Optimizing for Voice Search and Featured Snippets
With voice search becoming more popular, optimizing your content for conversational queries is important. Additionally, aim for featured snippets by structuring your content in a way that provides clear, concise answers to specific questions.
Tools to Optimize for Semantic SEO
To help streamline your semantic SEO efforts, consider using the following tools:
- Grocliq: Grocliq is an all-in-one SEO solution designed to simplify and automate SEO tasks, making it especially valuable for businesses, agencies, and freelancers.
- SEMrush: A powerful tool for keyword research and competitive analysis.
- Ahrefs: Helps discover LSI keywords and analyze your backlink strategy.
- Keyword Magic Tool: Generates related keywords for better content optimization.
- Clearscope: Optimizes content for better semantic understanding.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Semantic SEO
When implementing semantic SEO, it’s crucial to avoid common mistakes that can hurt your rankings and user experience. Here are some key pitfalls to watch out for:
- Overloading Content with LSI Keywords: Using latent semantic indexing SEO (LSI) keywords is important, but overuse can lead to keyword stuffing, which negatively impacts readability and rankings. Focus on integrating these keywords naturally.
- Ignoring Search Intent: Failing to align your content with the user’s search intent can reduce its relevance. Ensure your content matches whether the intent is informational, transactional, or commercial.
- Incorrect Schema Markup Implementation: Semantic markup SEO helps search engines understand your content. Incorrect or missing schema markup can prevent your content from appearing as rich snippets and affect rankings.
- Not Updating Old Content: Neglecting to refresh older content can cause it to lose relevance. Regularly update articles with new information, LSI keywords, and proper semantic markup.
- Overlooking Voice Search Optimization: Voice searches are conversational. Failing to optimize for them means missing out on opportunities to rank for long-tail, question-based queries.
- Prioritizing SEO Over User Experience: A well-optimized website must also offer a good user experience. Poor navigation, slow load times, or intrusive ads can hurt both rankings and user engagement.
- Ignoring Long-Tail Keywords: Long-tail keywords are highly relevant and less competitive. Semantic SEO thrives on using them to improve content context and attract targeted traffic.
- Failing to Track Performance: Semantic SEO is an ongoing process. Regularly track your content’s performance using tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to adjust and refine your strategy.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can improve your semantic SEO strategy, ensuring better rankings, higher user engagement, and long-term success.
Measuring Success in Semantic SEO
The success of your semantic SEO efforts can be measured through several key performance indicators (KPIs):
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Organic Traffic Growth: Monitor the increase in organic search traffic over time.
- Keyword Rankings: Track how your rankings for primary and secondary keywords improve.
- Engagement Metrics: Measure how users interact with your content, such as bounce rate and time on page.
Tracking Tools:
- Google Analytics: Provides insights into user behavior and traffic patterns.
- Google Search Console: Tracks the performance of your content in search results.
Conclusion
Semantic SEO is essential for staying ahead in today’s competitive search landscape. By focusing on latent semantic indexing SEO, semantic markup SEO, and understanding Google search semantics SEO, you can ensure your content is relevant, valuable, and properly optimized for search engines. Start using these strategies today to enhance your website’s visibility, improve rankings, and provide a better experience for your users.
Note: Read Our Latest Blogs:
What is Wix Analytics | What is B2C SEO | AI SEO Content Generator | AI is Transforming E-commerce | AI Semantic SEO | AI for SEO Optimization | AI SEO Prompts | Structured Content AI | What is Cluster AI SEO | AI SEO Software Tool | Will AI Replace SEO? | AI Content for SEO | How AI is Going to Change SEO | Automated AI SEO Tools | Local SEO AI
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is Semantic SEO, and how does it differ from traditional SEO?
Ans: Semantic SEO is about understanding user intent and context, while traditional SEO focuses solely on targeting specific keywords.
Q2. How does Google use semantic search to rank content?
Ans: Google analyzes the meaning behind search queries and ranks content that best matches the user’s intent, not just specific keywords.
Q3. What is Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) SEO?
Ans: LSI SEO helps search engines identify related words and phrases, improving content relevance and rankings.
Q4. What are the benefits of semantic markup SEO?
Ans: Semantic markup SEO enhances content visibility in search engines by providing structured data that helps search engines better understand the content.
Q5. How can I optimize my content for voice search with semantic SEO?
Ans: Use a conversational tone and focus on answering specific questions directly to optimize for voice search.
Q6. What tools can I use for semantic SEO?
Ans: Tools like SEMrush, Grocliq, and Ahrefs help optimize your content for semantic SEO.
Q7. What are the key principles of semantic SEO?
Ans: Understanding search intent, using semantic markup SEO, and integrating LSI keywords are key principles.
Q8. How do I track the success of my semantic SEO efforts?
Ans: Use tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to monitor traffic, rankings, and user engagement.